A Simple Explanation of VNG Testing for Patients

Videonystagmography (VNG) testing is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the balance system and ear function by measuring involuntary eye movements called nystagmus.
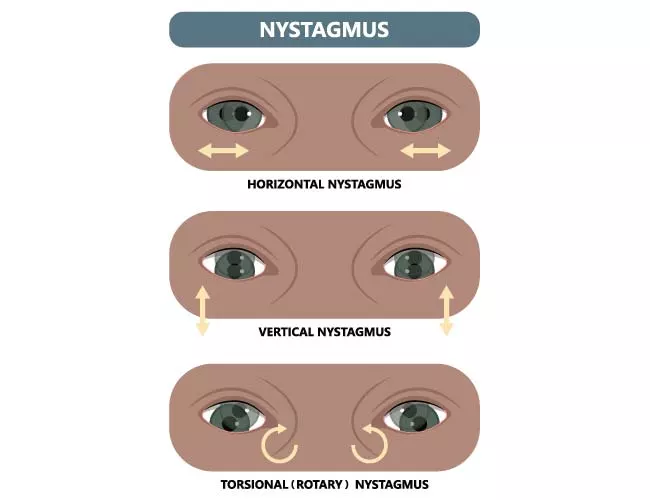
Nystagmus refers to repetitive, uncontrolled eye movements, which may result from inner ear disorders, neurological conditions, or medication side effects.
By performing a VNG test, clinicians can record and analyze eye movement patterns to determine the underlying cause of a patient’s dizziness or balance issues.
VNG testing is a critical tool in diagnosing various vestibular and neurological conditions, including:
VNG testing consists of multiple subtests to assess the vestibular nerve and overall balance system. During the test, patients wear VNG goggles equipped with infrared cameras that track eye movements. The patient is guided through several tasks, including:
By recording and analyzing eye movements in response to these stimuli, clinicians can identify vestibular disorders affecting the inner ear or brain.
Preparing for a VNG test involves avoiding certain medications, caffeine, and alcohol for at least 24 hours before the procedure. Patients should wear comfortable clothing and arrange transportation, as dizziness may occur after testing.
During the test, the patient sits in a chair while wearing VNG goggles. The test takes approximately 30–60 minutes. Some patients may experience brief dizziness or nausea, but these symptoms usually subside quickly.
VNG testing is a safe and effective way to diagnose vestibular disorders. Its benefits include:
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to complement VNG testing:
Caloric testing: Measures vestibular function using warm or cool air or water.
Evoked potentials: Evaluates brain activity in response to sensory stimuli.
CT or MRI scans: Helps detect structural issues such as tumors or brain injuries.
For practitioners looking to expand their diagnostic capabilities, investing in a high-quality VNG system is essential. When selecting a system, consider:
If you’re interested in learning more about VNG testing equipment, contact e3 Diagnostics today to explore our solutions and find the right fit for your practice.